Her 2 positive Breast Cancer
What is HER2-Positive Breast Cancer?
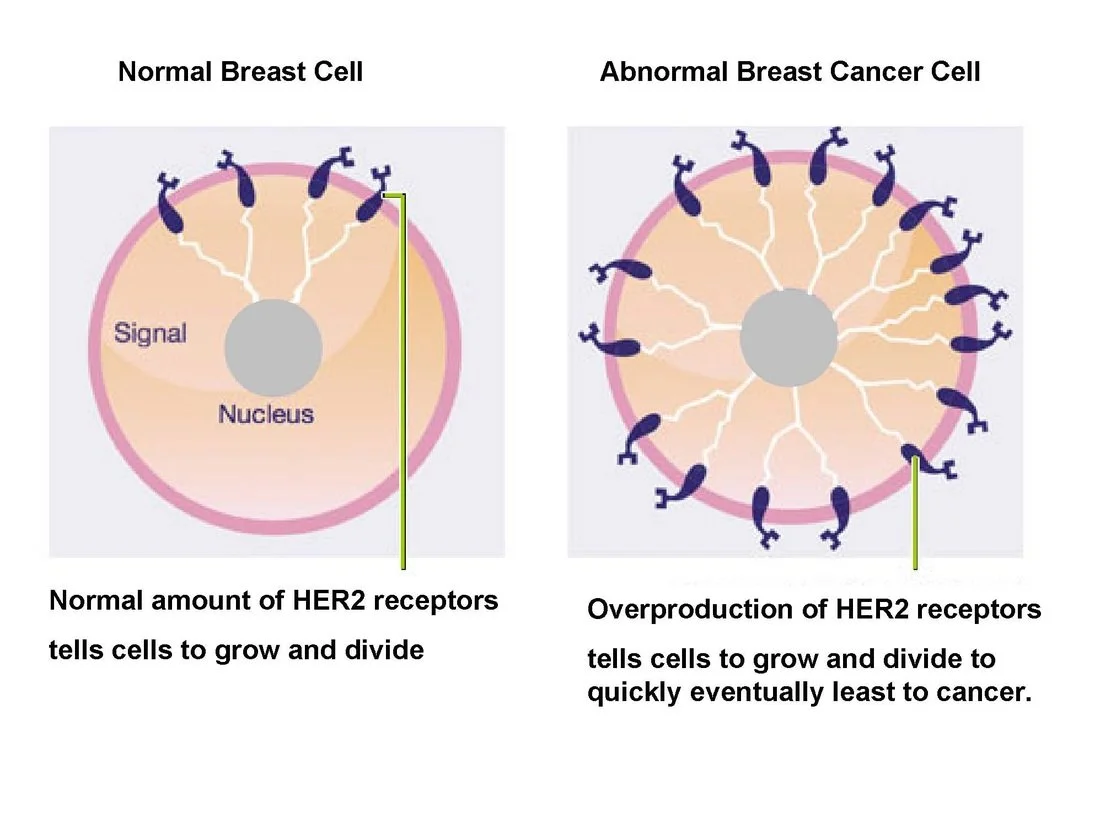
HER2-Positive Breast Cancer is a type of breast cancer where cancer cells have an overexpression of the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) protein. HER2 promotes cell growth, and when it’s overproduced, it can cause cells to grow and divide more rapidly, contributing to the spread of cancer.
HER2-positive breast cancer is considered an aggressive form of breast cancer. However, targeted treatments have greatly improved outcomes for people with HER2-positive breast cancer.
Who is at Risk?
HER2-positive breast cancer can affect anyone, but factors that might increase the risk include:
Age – This type of breast cancer can appear at any age, though it’s more common in younger women.
Genetic Factors – Although rare, certain genetic mutations may increase the likelihood of developing HER2-positive breast cancer.
How is HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Diagnosed?
The diagnostic process includes:
Breast Examination – Your healthcare provider checks for lumps or changes.
Imaging Tests – Mammograms, ultrasounds, CTs or MRIs are used to examine the breast tissue.
Biopsy – A small tissue sample is taken and tested to confirm the presence of HER2 proteins on cancer cells. The two common tests used to determine HER2 status are:
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) – Measures the amount of HER2 protein on cancer cells.
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) – Looks for extra copies of the HER2 gene in cancer cells.
Treatment Options for HER2-Positive Breast Cancer
There are several effective treatments specifically targeting HER2-positive breast cancer. These may be used alone or in combination, depending on the individual case.
1. Targeted Therapy
Trastuzumab (Herceptin) – A monoclonal antibody that targets HER2 proteins, blocking signals that cause cancer cells to grow.
Pertuzumab (Perjeta) – Often used alongside trastuzumab, especially for advanced HER2-positive breast cancer.
Ado-trastuzumab emtansine (Kadcyla) – A combination of trastuzumab and chemotherapy that targets HER2-positive cancer cells while delivering chemotherapy directly to them.
2. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is often combined with targeted therapies to kill rapidly dividing cancer cells and help prevent recurrence. It may be administered before (neoadjuvant) or after surgery (adjuvant).
3. Surgery
Lumpectomy – Removes only the tumour and a small margin of surrounding tissue.
Mastectomy +/- reconstruction – Removes one or both breasts if the cancer is more widespread.
Lymph Node Removal – Checks if the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes.
4. Radiation Therapy
Radiation may be recommended after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells in the breast or chest area, reducing the chance of recurrence.
Managing Life with HER2-Positive Breast Cancer
Side Effects of Treatment: Side effects may include fatigue, nausea, heart-related issues, and hair loss. Your healthcare team can help manage these effects with supportive therapies.
Follow-up Care: Regular follow-up visits with your healthcare provider are essential to monitor for any signs of recurrence. Follow-up care often includes imaging, physical exams, and blood tests.
Lifestyle Support: Staying active, eating a nutritious diet, and practicing stress-relief techniques can help maintain physical and emotional health.
Support and Resources
HER2-positive breast cancer can be challenging, but support is available:
Support Groups – Local and online groups can connect you with others going through similar experiences.
Cancer Support Services – Hospitals often offer counseling, physical therapy, and nutrition support.
You will have a Breast Care Nurse as part of your journey through breast cancer treatment. Their role is to guide you through the maze of appointments and treatments, to be a source of emotional and physical support and your point of contact for questions and concerns now and in the future.
Questions for Your Doctor
What stage is my HER2-positive breast cancer, and what does this mean?
What treatment options are best for my situation?
What are the potential side effects of treatment?
Are there clinical trials that could be beneficial?
Remember: Many people with HER2-positive breast cancer live full, healthy lives after treatment. Advances in targeted therapies have improved survival rates and quality of life for those with HER2-positive breast cancer.